Inventory App - Android Mobile Application
CS360 Mobile Architecture and Programming
Software Design and Engineering Category
The Inventory application tracks items in an inventory list through the primary use of mobile devices. For example, the track of the items through the app at a warehouse assists in managing and automating the warehouse logistics and accelerating the business’s growth and expansion. The app allows the user to fulfill anywhere experience with real-time inventory visibility on any device. The app development is initially based on an installation for Android Devices.
My approach to coding the mobile app was to develop it in JAVA programming language with a minimum Android SDK API 16 (Jelly Bean). The API 16 allows the app to run on approximately 99.8% of the devices. I look for help from collaborators in resolving programmatic problems during the development and integration of the design. The source code is strategically implemented for the app development. It is of much gratification and helpful experience to work on my ideas with a good collaboration team than doing it on our own, limiting our knowledge and experience and the growth of our concept.

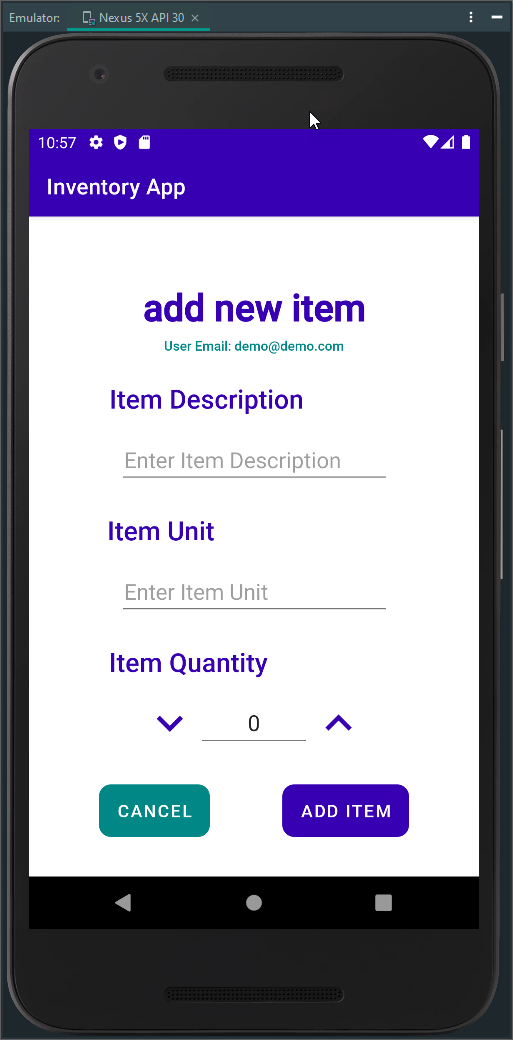
Figure 1 - Items Activity and Add Item Activity Screenshot
I employed industry-standard JAVA code best practices and techniques such as in-line comments, appropriate naming conventions, formatting, and indentation in conformance with proper coding standards, making the code easy to read and enhancing the application code organization. JAVA class files were named with camelCase CapWords and layout files with lower case names. Global variables are named with camelCase CapWords names, and class methods scope variables are named with camelCase lower case names or lower case dash_names. The class methods naming, as possible, are a representation of the method’s purpose and action. Comments statements in the code summaries class and methods functionality. Methods that override methods from its superclass are named camelCase with an initial lower case word. Other ways that do not override methods from its superclass are named in camelCase with CapWords.
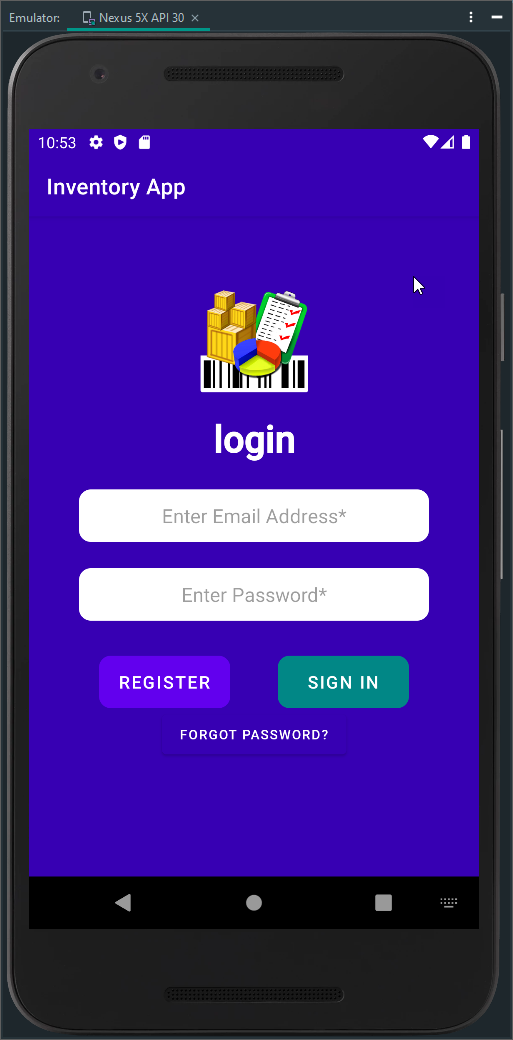
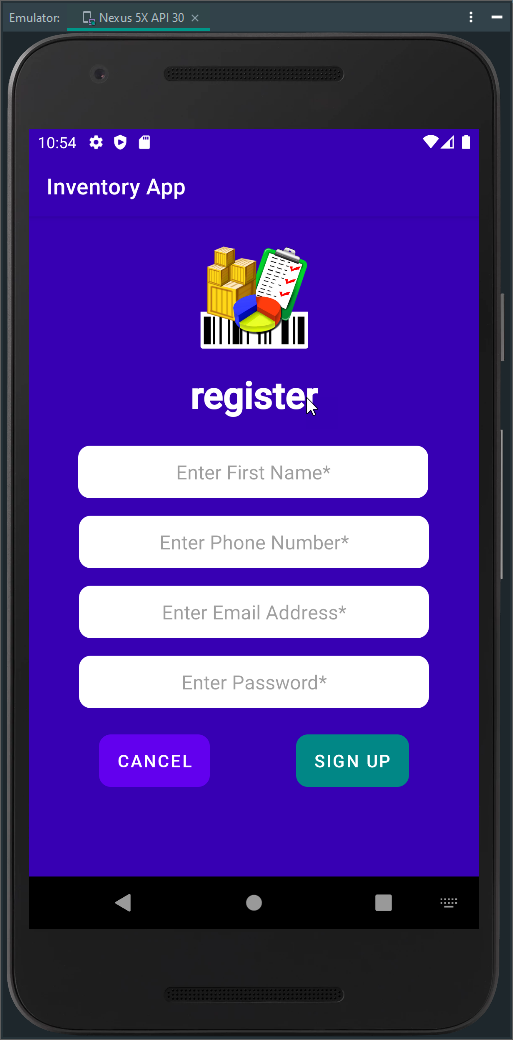
Figure 2 - Login Activity and Register Activity Screenshot
Their name and email authenticate the user as part of their login credentials, and their phone number is used to recover their password in case of forgetting. These features showcased our zero-trust ethic and emphasized our security mindset in the development process to anticipate adversarial exploits in software architecture and designs to expose potential vulnerabilities, mitigate design flaws, and ensure privacy and enhanced security of data and resources. We conduct security from initiation, product assuredness, testing, and compatibility checks in our entire software development life cycle. Apply secure coding standards for the target development language and platform.
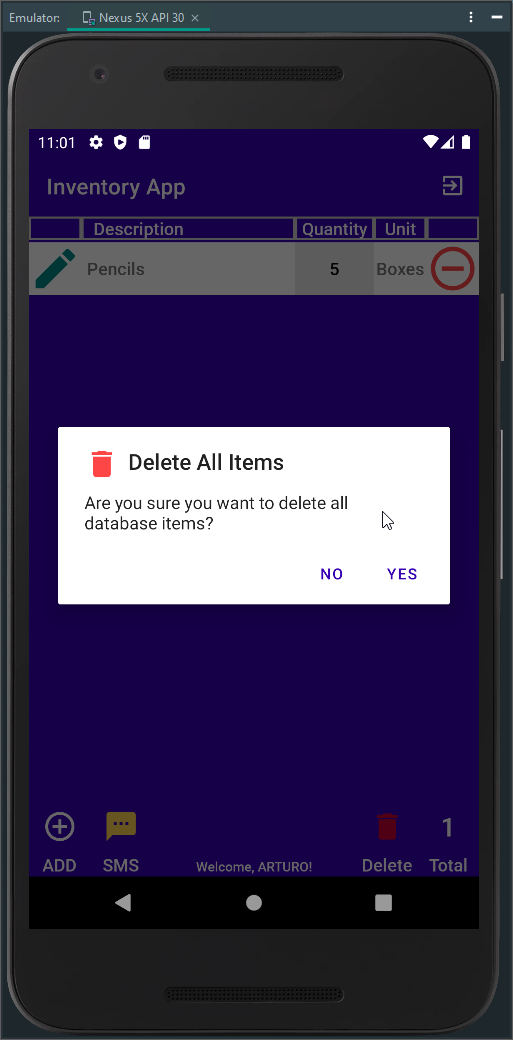
Figure 3 - Delete Items Alert Dialog and App Info Screenshot
Through the design and development of the components for the mobile app using the Android Studio IDE, I am particularly successful in demonstrating my knowledge, skills, and experience in understanding the relations of the activities and their elements and how to integrate them with the programmatic phase of the mobile app. I apply mobile development principles and best practices to develop mobile applications using user-centered design principles and industry standards. I conduct security, product assuredness, and compatibility checks before launching the application.
Artifact enhancement files repository at CS360 Mobile Architecture and Programming




